University MySQL Database
27 Jun 2017Content:
- 1. Requirement Overview
- 2. Data Storage Solution
- 3. Illustration of the design
- 4. Scripts for data storage
- 5. Main usage and Scripts for typical use cases
- 6. Scripts and Report
DESIGN REPORT FOR UNIVERSITY DATABASE
1. Requirement Overview
The government of Vietnam planned to build a new university in a small town, they hired a team of 3 IT engineers to build a completely new data storage to keep track of information, especially about students and their score so that a wide range of scholarship from different providers will be given to students with hardship but still can maintain decent academic records. As being a small-scale university, the client wants to have data storage solution which strongly focus on different information of students. Here are the necessary requirement from the client:
- Storage solution that have strong focus on different relation between objects and roles.
- Keep track of students grade for different subjects, their number of attempt.
- Information about the class that they have enrolled.
- The class mentioned in previos requirement include staff’s information including tutors and conveners.
- Conveners must a faculty member of the university, one faculty can have more than one convener and one convener can work for more than one faculty.
- Tutors and Conveners as considered as employee of the university, they have rank which determines the pay rate each month.
- This new university will have a limited number of room so it’s compulsory to keep track of the room for each class, multiple rooms for different teaching sessions is allowed.
- Room number will be the same as room indentification number, they must be a 3 character string.
- Keep track of scholarship for each student and the provider of each scholarship as well as a field to keep the amount, requirement of scholarship. The project is currently looking to more funding, they want to hire as low as IT engineers as possible. Therefore, they want a clear design report which demonstrate the design of the data storage solution, the scripts need to be clear, easy to read, and well-documented. They also want to have a very wide range of example main usage so that other developer can develope the functionality upon the examples.
2. Data Storage Solution
In this project, I decide to use a relational database MySQL to tackle the requirements from client. This relational database is widely used, easy to use, extremely powerful, secure and scalable. Strong entity of database:
| Table name | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Student | Storing student personal information, their scholarship and faculty |
| 2 | Faculty | Name and ID of faculty where convener and student belongs, this section will be extended on request |
| 3 | Subject | The subject name and ID, they also record the prerequisite of a subject so that we can check if a student can enroll or not, it also can store requirement information and credit worth. |
| 4 | Class | Class ID and convener ID who is responsible for the class, one subject can have multiple class. |
| 5 | Result | This table store results of students, the score for the unit they have taken as well as the number of attempt they took. |
| 6 | Room | Room details, including number, location, condition, size and whether it’s reserved or not. Room has relation with class. Class must be allocated to different room because of the small number of room in the new university |
| 7 | Convener | Convener details, they are the one who is mainly responsible for the classes that are assigned. They also have rank which determine their pay rate |
| 8 | Tutor | Tutors are the one who help convener convey the information in the lecture as well as running the lab. They also have rank which determine their pay rate |
| 9 | Salary | Store pay rate of rank, it is separated table, not merged into each staff because changing pay rate for a rank can applied for every staffs, we don’t have to change individual staff pay rate if pay rate are applied to staff individually |
| 10 | Scholarship | Grants and Scholarship of students, they have ID and Value as well as condition to maintain the funding. |
| 11 | Provider | This table stores provider which rasing fund and scholarship for student. One provider can have multiple scholarship for student |
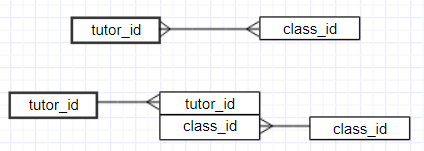
Dealing with many to many relationship: For many to many relationship, there is a weak entity between them so that a many to many relationship becomes 2 one to many relationship. For example, in this project, Tutor_Class, Scholarship_Provider and Faculty_convener are weak entity, they are junction table. One tutor can teach more than one class and one class can have more than one tutor.
Data type:
- Every ‘ID’ will be a 3-character string except ‘Faculty ID’. ‘Faculty ID’ is a 2-character string.
- ‘Genders’ are stored as ‘male’ or ‘female’.
- Date of birth or dob is stored as DATE type. They have the following format: YYYY/MM/DD. A correct format for date is required.
- ‘Credit’ in ‘Subject’ table will be a decimal number which display exaclty 3 digits, one after the comma.
- Score is stored as an integer ranging from 0 to 100, scholarship value is integer type.
- Other field will accept any string which have less than 30 characters.
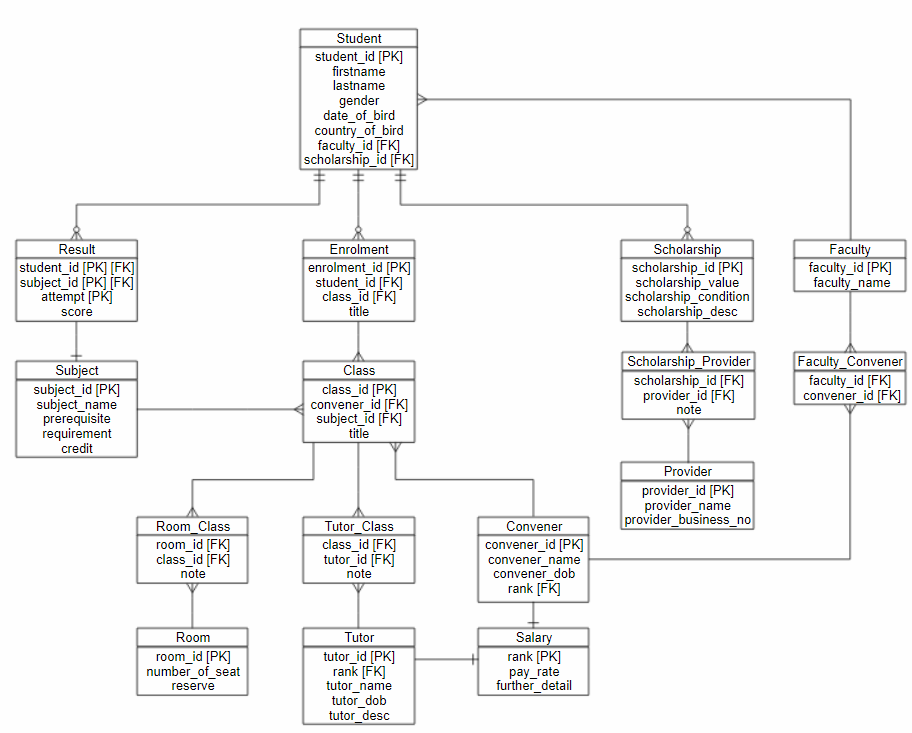
3. Illustration of the design
4. Scripts for data storage
/*=====================Falculty table===================*/
CREATE TABLE Faculty
(
faculty_id char(2) PRIMARY KEY,
faculty_name nvarchar(30) NOT NULL
);
/*=====================Student table===================*/
DROP TABLE Student;
CREATE TABLE Student
(
student_id char(3) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
firstname nvarchar(30) NOT NULL ,
lastname nvarchar(30) NOT NULL ,
gender enum('male', 'female' , 'homo'),
date_of_birth date NOT NULL ,
country_of_bird nvarchar(20),
faculty_id char(2),
scholarship_id char(3)
);
/*=====================Subject table===================*/
CREATE TABLE Subject
(
subject_id char(3) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
subject_name nvarchar(25) NOT NULL ,
prerequisite nvarchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
requirement nvarchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
credit decimal(3,1) /* 3 digits in total, 1 digit after the comma */
);
/*===================== Result table===================*/
CREATE TABLE Result
(
student_id char(3) NOT NULL,
subject_id char(3) NOT NULL,
attempt int DEFAULT 1,
score int,
PRIMARY KEY (student_id, subject_id, attempt)
);
/*===================== Enrolment table===================*/
CREATE TABLE Enrolment
(
enrolment_id char(3) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
student_id char(3) NOT NULL,
class_id char(3),
title nvarchar(30)
);
/*===================== Class table===================*/
CREATE TABLE Class
(
class_id char(3) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
convener_id char(3) NOT NULL,
subject_id char(3) NOT NULL,
title nvarchar(30)
);
/*===================== Class table===================*/
CREATE TABLE Room_Class
(
room_id char(3),
class_id char(3),
note nvarchar(30)
);
/*===================== Room table===================*/
CREATE TABLE Room
(
room_id char(3) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
number_of_seat int NOT NULL,
reserve bool DEFAULT False
);
/*===================== Tutor table===================*/
CREATE TABLE Tutor
(
tutor_id char(3) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
rank char(3),
tutor_name nvarchar(30) NOT NULL,
tutor_dob date NOT NULL,
tutor_desc nvarchar(30)
);
/*===================== Tutor_Class table===================*/
CREATE TABLE Tutor_Class
(
class_id char(3) NOT NULL,
tutor_id char(3) NOT NULL,
note nvarchar(30)
);
/*===================== Convener table===================*/
CREATE TABLE Convener
(
convener_id char(3) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
rank char(3),
convener_name nvarchar(30),
convener_dob date
);
/*===================== Faculty_Convener table===================*/
CREATE TABLE Faculty_Convener
(
convener_id char(3) NOT NULL,
faculty_id char(2) NOT NULL
);
/*===================== Salary table===================*/
CREATE TABLE Salary
(
rank CHAR(3) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
pay_rate decimal(6,3),
further_detail nvarchar(30)
);
/*===================== Scholarship table===================*/
CREATE TABLE Scholarship
(
scholarship_id char(3) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
scholarship_value int(6) NOT NULL,
scholarship_condition nvarchar(30),
scholarship_desc nvarchar(30)
);
/*===================== Provider table===================*/
CREATE TABLE Provider
(
provider_id CHAR(3) PRIMARY KEY,
provider_name nvarchar(30) NOT NULL,
provider_business_no INT(6) NOT NULL
);
/*===================== Scholarship_Provider table===================*/
CREATE TABLE Scholarship_Provider
(
scholarship_id char(3) NOT NULL,
provider_id char(3) NOT NULL,
note nvarchar(30)
);
/*===================== Foreign Key===================*/
/*==========Student=========*/
ALTER TABLE Student
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Student_Faculty
FOREIGN KEY (faculty_id) REFERENCES Faculty (faculty_id);
ALTER TABLE Student
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Student_Scholarship
FOREIGN KEY (scholarship_id) REFERENCES Scholarship (scholarship_id);
/*=========Result===========*/
ALTER TABLE Result
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Result_Student
FOREIGN KEY (student_id) REFERENCES Student (student_id);
ALTER TABLE Result
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Result_Subject
FOREIGN KEY (subject_id) REFERENCES Subject (subject_id);
/*=========Enrolment========*/
ALTER TABLE Enrolment
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Enrolment_Student
FOREIGN KEY (student_id) REFERENCES Student (student_id);
ALTER TABLE Enrolment
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Enrolment_Class
FOREIGN KEY (class_id) REFERENCES Class (class_id);
/*=========Scholarship_Provider======*/
ALTER TABLE Scholarship_Provider
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Scholarship_Provider
FOREIGN KEY (scholarship_id) REFERENCES Scholarship (scholarship_id);
ALTER TABLE Scholarship_Provider
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Provider_Scholarship
FOREIGN KEY (provider_id) REFERENCES Provider (provider_id);
/*==========Class==========*/
ALTER TABLE Class
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Class_Convener
FOREIGN KEY (convener_id) REFERENCES Convener (convener_id);
ALTER TABLE Class
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Class_Subject
FOREIGN KEY (subject_id) REFERENCES Subject (subject_id);
/*===========Room_class===========*/
ALTER TABLE Room_Class
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Room_Class
FOREIGN KEY (room_id) REFERENCES Room (room_id);
ALTER TABLE Room_Class
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Class_Room
FOREIGN KEY (class_id) REFERENCES Class (class_id);
/*============Convener============*/
ALTER TABLE Convener
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Convener_Salary
FOREIGN KEY (rank) REFERENCES Salary (rank);
/*=============Tutor_Class==========*/
ALTER TABLE Tutor_Class
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Tutor_Class
FOREIGN KEY (tutor_id) REFERENCES Tutor (tutor_id);
ALTER TABLE Tutor_Class
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Class_Tutor
FOREIGN KEY (class_id) REFERENCES Class (class_id);
/*===============Tutor==============*/
ALTER TABLE Tutor
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Tutor_Salary
FOREIGN KEY (rank) REFERENCES Salary (rank);
/*================Faculty_Convener==============*/
ALTER TABLE Faculty_Convener
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Faculty_Convener
FOREIGN KEY (faculty_id) REFERENCES Faculty (faculty_id);
ALTER TABLE Faculty_Convener
ADD CONSTRAINT fk_Convener_Faculty
FOREIGN KEY (convener_id) REFERENCES Convener (convener_id);
5. Main usage and Scripts for typical use cases
/*=====================Test Data===================*/
/*==============Test data Subject =============*/
INSERT INTO Subject (subject_id, subject_name , credit)
VALUES ('A01', 'database system',45);
INSERT INTO Subject (subject_id, subject_name , credit)
VALUES ('B02', 'artificial intelligent',45);
INSERT INTO Subject (subject_id, subject_name , credit)
VALUES ('C03', 'programming',45);
INSERT INTO Subject (subject_id, subject_name , credit)
VALUES ('D04', 'graphical design',60);
INSERT INTO Subject (subject_id, subject_name , credit)
VALUES ('E05', 'biology',60);
SELECT * FROM Subject;
/*==============Test data Faculty =============*/
INSERT INTO Faculty ( faculty_id , faculty_name)
VALUES ('AV', 'Engineering');
INSERT INTO Faculty ( faculty_id , faculty_name)
VALUES ('TH', 'Information Technology');
INSERT INTO Faculty ( faculty_id , faculty_name)
VALUES ('TR', 'Phylosophy');
INSERT INTO Faculty ( faculty_id , faculty_name)
VALUES ('VL', 'Physic');
SELECT * FROM Faculty;
/*==============Test data Scholarship=========*/
INSERT INTO Scholarship( scholarship_id, scholarship_value, scholarship_condition)
VALUES (130, 100000, 'no fail unit');
INSERT INTO Scholarship( scholarship_id, scholarship_value, scholarship_condition)
VALUES (150, 200000, 'at least pass all');
INSERT INTO Scholarship( scholarship_id, scholarship_value, scholarship_condition)
VALUES (170, 300000, 'HD on every unit');
/*==============Test data Student=============*/
INSERT INTO Student( student_id , firstname , lastname , gender , date_of_birth , country_of_bird, faculty_id ,scholarship_id)
VALUES ('A01', 'Andrew', 'Ng', 'female' ,'1994/12/12', 'Melbourne','TH',130);
INSERT INTO Student( student_id , firstname , lastname , gender , date_of_birth , country_of_bird, faculty_id ,scholarship_id)
VALUES ('A02', 'Geoff', 'Hinton', 'male','1994/06/22', 'Sydney','VL',150);
INSERT INTO Student( student_id , firstname , lastname , gender , date_of_birth , country_of_bird, faculty_id ,scholarship_id)
VALUES ('A03', 'Joshen', 'Joe', 'female','1995/03/24', 'Canberra','TH',170);
INSERT INTO Student( student_id , firstname , lastname , gender , date_of_birth , country_of_bird, faculty_id)
VALUES ('A04', 'Palo', 'Kai', 'male','1994/03/14', 'Melbourne','AV');
INSERT INTO Student( student_id , firstname , lastname , gender , date_of_birth , country_of_bird, faculty_id)
VALUES ('B01', 'Kaio', 'Sing', 'female','1994/11/01', 'Melbourne','TR');
INSERT INTO Student( student_id , firstname , lastname , gender , date_of_birth , country_of_bird, faculty_id)
VALUES ('B02', 'andrew', 'a', 'female','1994/01/22', 'Melbourne','AV');
SELECT * FROM Student;
/*====================Test data Result==================*/
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('A01','A01',1,3);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('A01','A01',2,6);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('A01','B02',2,6);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('A01','C03',1,5);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('A02','A01',1,4.5);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('A02','A01',2,7);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('A02','C03',1,10);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('A02','E05',1,9);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('A03','A01',1,2);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('A03','A01',2,5);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('A03','C03',1,2.5);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('A03','C03',2,4);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('A04','E05',2,10);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('B01','A01',1,7);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('B01','C03',1,2.5);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('B01','C03',2,5);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('B02','B02',1,6);
INSERT INTO Result (student_id,subject_id,attempt,score)
VALUES ('B02','D04',1,10);
SELECT * FROM Result;
/*====================Test data Provider==================*/
INSERT INTO Provider (provider_id, provider_name, provider_business_no)
VALUES ('P01', 'government', 111221);
INSERT INTO Provider (provider_id, provider_name, provider_business_no)
VALUES ('P02', 'monash provider', 412321);
INSERT INTO Provider (provider_id, provider_name, provider_business_no)
VALUES ('P03', 'swinburne provider', 221921);
INSERT INTO Provider (provider_id, provider_name, provider_business_no)
VALUES ('P04', 'Latrobe Uni provider', 114223);
SELECT * FROM Provider;
/*=====================Test data Scholarship_Provider*/
INSERT INTO Scholarship_Provider (scholarship_id, provider_id)
VALUES (130, 'P01');
INSERT INTO Scholarship_Provider (scholarship_id, provider_id)
VALUES (150, 'P03');
INSERT INTO Scholarship_Provider (scholarship_id, provider_id)
VALUES (150, 'P03');
Some typical usage:
- Update information
UPDATE … SET … WHERE DELETE … FROM … WHEREExample: Change credit point worth of subject with subject_id A01
UPDATE Subject SET credit = 12.5 WHERE subject_id = 'C03';Change firstname and lastname of student
UPDATE Student SET firstname = 'Andrew', lastname = 'Lai' WHERE student_id = 'A02'Delete entire row of Result table where number of attemp is equal 2 and score is less than 25
DELETE FROM Result WHERE attempt = 2 and score < 25NOTE: It’s impossible to update a parent row where the parent is affected by a foreign key, for example, the following command will not be executed:
DELETE FROM Student WHERE scholarship_id = 130The reason is that Student table is a parent of Scholarship table and they are connected by scholarship_id, if we want to change student scholarship, we need to change it from scholarship_table:
DELETE * FROM Scholarship WHERE Schoalrship_id = 130 - Viewing data with simple querry
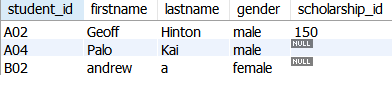
Viewing information of student in a table using
SELECTcommand, name are listed by student IDSELECT student_id as 'Student ID', firstname as 'First name', lastname as 'Last name', scholarship_id as 'Scholarship ID' FROM Student ORDERBY student_id ASC
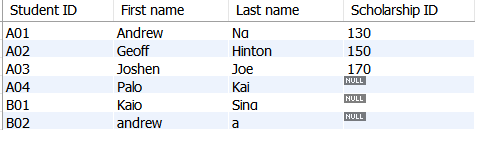
SELECT student_id AS 'Student ID', CONCAT(firstname,' ',lastname) as'Student full name',gender as 'Gender', date_of_birth as 'DOB'
FROM Student
ORDER BY gender ASC;
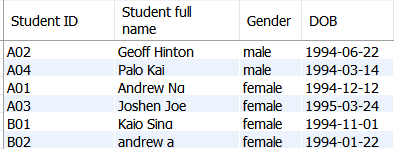
Note: It’s also possible to view male student or female student only by adding a WHERE condition: WHERE gender = ‘male’
- Viewing data with join command, join 2 tables
The following command listed all student that have scholarship and their scholarship value is more than 100000 dollars
SELECT st.student_id AS 'Student ID', CONCAT(st.firstname,' ',st.lastnawweame) as'Student full name', sc.scholarship_value as 'Scholarship value' FROM Student AS st NATURAL JOIN Scholarship as sc WHERE sc.scholarship_value > 100000 ORDER BY st.student_id ASC;

- Checking not exist data
The following command returns all student that fail 0 unit. (All score need to more more than 5)
SELECT student_id FROM Student s WHERE NOT EXISTS ( SELECT * FROM Result WHERE score<=5 AND student_id=s.student_id );
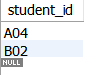
- Union two select commands with COUNT, HAVING, GROUP BY
Return the faculty that have the largest number of student having scholarship and faculty with smallest number of student having scholarship.
Select faculty_id,count(student_id) as 'Number of student' From Student Where scholarship_id is not null GROUP BY faculty_id Having count(student_id) >= All(Select count(student_id) From Student Where scholarship_id is not null Group By faculty_id ) UNION Select faculty_id,count(student_id) as 'Number of student' From Student Where scholarship_id is not null GROUP BY faculty_id Having count(student_id)<=All(Select count(student_id) From Student Where scholarship_id is not null Group By faculty_id ); - Create VIEW
View is a new table but the different is that this table is readonly.
Example: Create a view called Student_no_fail_unit that contains information about student that fails no unit.
CREATE VIEW Student_no_fail_unit AS SELECT Student.student_id , firstname, lastname , gender, scholarship_id FROM Student, Result WHERE Student.student_id = Result.student_id GROUP BY Student.student_id , firstname, lastname , gender, scholarship_id HAVING MIN(score)>=5;It’s possible to read this table as usual, for example:
SELECT * FROM Student_no_fail_unit;